The year of 2009 saw the dawn of a new revolution. Blockchain - the innovative backbone technology behind Bitcoin - emerged as a potentially disruptive force capable of transforming the financial services industry.
Since Bitcoin’s launch in 2009, blockchain has received widespread attention for a plethora of use-cases in and beyond the financial industry. Ten years after, a wide array of governments and industry players are placing blockchain on top of their strategic agendas. Their goal is to leverage blockchain’s potential to provide a reliable alternative to existing costly and inefficient operational models that depend on intermediaries to verify, distribute and synchronize transactions across business partners.
At its simplest terms, the blockchain technology features a replicated/distributed ledger consisting of a chain of all transactions across a peer-to-peer network. Each node in the network owns a full identical copy of the ledger, thus enforcing data sharing rather than data exchange.
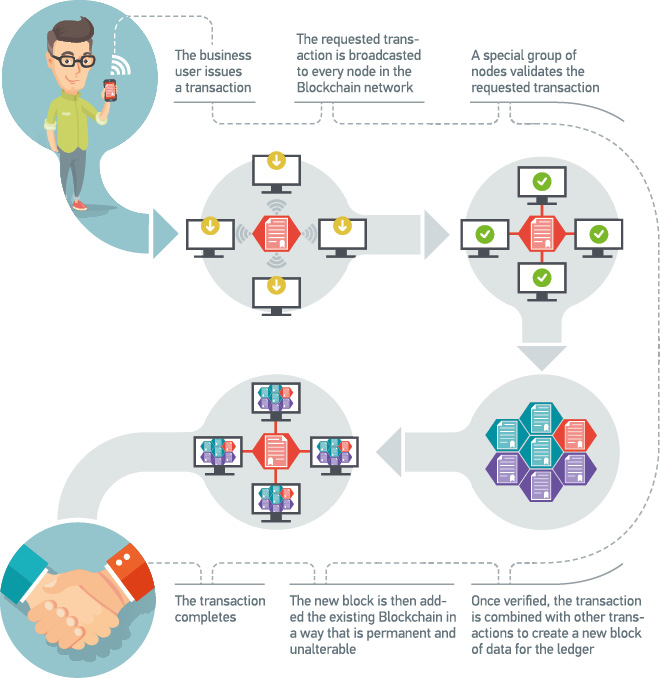
Anatomy of Typical Blockchain Transaction
Security is a key integral property of blockchain. For permissioned business networks, blockchain's access management facilities assure legitimate transactions, meaning that only identified users can join the network and specific authorization policies can be defined based on the user certificate attributes. Furthermore, blockchain’s advanced cryptographic techniques create a perpetual and immutable record of all transactions across the network, and all changes are auditable through signing. Specifically for use-cases subject to data confidentiality requirements, blockchain offers encryption and selective data distribution mechanisms for protecting private data.
Blockchain’s true uniqueness, however, lays in its two key design attributes: (1) one shared (smart contract) implementation, and (2) universal and synchronous data transparency for all participants to the same data source. In blockchain, the business logic is collectively and simultaneously executed, enforced and endorsed by the blockchain members who run the smart contract, thus promoting process integrity, business certainty and trust. Moreover, thanks to their embedded automated data distribution features and single (shared) data infrastructure, blockchain-based solutions are expected to foster more transparent, efficient, and less costly operations.
INTRASOFT International is already active on blockchain, exploring the technical applicability of the technology and the potential efficiencies that it could release in various use-cases, such as Customs and Taxation trade facilitation, Insurance and Banking, among other. Current results are encouraging and a rich portfolio of research activities is already planned to further develop our knowledge on blockchain in numerous critical areas, such as data confidentiality, network deployment, network re-configuration, scalability and performance.
Stay tuned for more!
Author: Vivi Armata.

